GitLab CI: Auto dependency updates
The problem
Using components with known vulnerabilities is one of the top ten web application security risks of the famous OWASP Top Ten list. It is easy to forget to update your dependencies of your projects if this is a manual process. I am working in a small team (3 people) and we have to manage/maintain and program multiple services. For example some of our services are programmed in Python. All requirements we are using are pinned to a specific version, so every time we build our docker image the same packages are installed. However, if a service is completed or no more work is currently required its pretty easy to forget to update the pinned versions in the requirements file. If this would be the case our services may have known vulnerabilities that were already fixed and the chances of a successful attack would be higher.
The solution
However, this process can be automated using GitLab and there great CI/CD integration. GitLab’s pipelines let you automate steps like builds, tests, and deployments. GitLab pipelines are normally run based on certain conditions met, e.g. if you push your code. However, you can also schedule pipelines at specific intervals. For example every Monday at 5 a.m. or once a day.
In your projects sidebar navigate to CI / CD > Schedules.
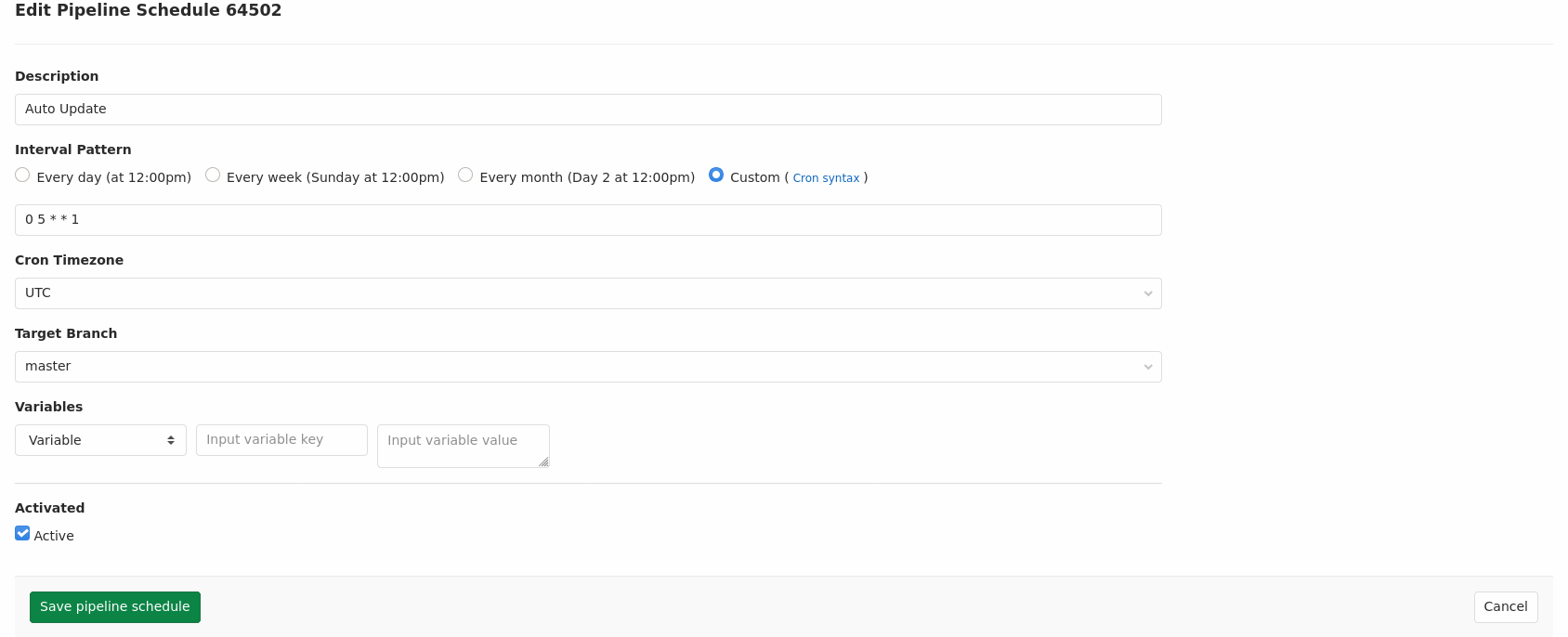
Then click on New schedule button and fill out the form and save it. I choose the master branch as my target branch and scheduled the pipeline for every Monday at 5 a.m.
When the scheduled pipeline is run I want to create a merge request if any package could be updated.
1# .gitlab-ci.yml
2bot:
3 # only run if this is a scheduled pipeline
4 only:
5 - schedules
6
7 image: python:3.8
8
9 script:
10 - cd $CI_PROJECT_DIR
11 # Checkout to a new branch so we push the changes to a new branch
12 - git checkout -b auto-update-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d')
13 - apt-get install -qy curl
14 # We are using pip-tools to handle/pin our dependencies
15 - pip install pip-tools
16 - chmod 700 update.sh
17 # This script updates my requirements file.
18 # This can be customized however you want to fit your needs.
19 - ./update.sh
20 # If any line was changed then commit the changes, push them and create a merge request
21 - |
22 lines=$(git status -s | wc -l)
23 if [ $lines -gt 0 ];then
24 echo "committing"
25 git config --global user.name "${AUTO_COMMITTER_NAME}"
26 git config --global user.email "${AUTO_COMMITTER_EMAIL}"
27 git add .
28 git commit -m "auto-update-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d')"
29 git push "https://${GITLAB_USER_NAME}:${GIT_PUSH_TOKEN}@${CI_REPOSITORY_URL#*@}"
30 BODY="{\"id\": \"${CI_PROJECT_ID}\", \"source_branch\": \"auto-update-$(date '+%Y-%m-%d')\", \"target_branch\": \"master\", \"remove_source_branch\": true, \"title\": \"Auto Update $(date '+%Y-%m-%d')\"}"
31 curl -X POST "https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/${CI_PROJECT_ID}/merge_requests" \
32 --header "PRIVATE-TOKEN:${GIT_PUSH_TOKEN}" \
33 --header "Content-Type: application/json" \
34 --data "${BODY}";
35 echo "Opened a new merge request: \"Auto Update $(date '+%Y-%m-%d')\" and assigned to you";
36 exit;
37 else
38 echo "no change, nothing to commit"
39 fi
40
41test:
42 stage: test
43
44 # dont run if this is a scheduled pipeline
45 except:
46 - schedules
47 ...The update.sh script is responsible to update the requirements file and pin the newest version of each package. We are using pip-tools to handle/pin our dependencies. It’s a great tool. You only need to define you packages you want to install and it automatically pinns the newest version of this packages and the packages dependencies in a requirements.txt file. It makes it super easy to use pinned packages.
For example your update.sh script could be as simple as the following. This will generate up-to date pinned requirements files.
1#!/bin/bash
2# update.sh
3pip-compile --upgrade requirements/*.in -o requirements/all.txt
4pip-compile --upgrade requirements/base.in requirements/tests.in -o requirements/tests.txt
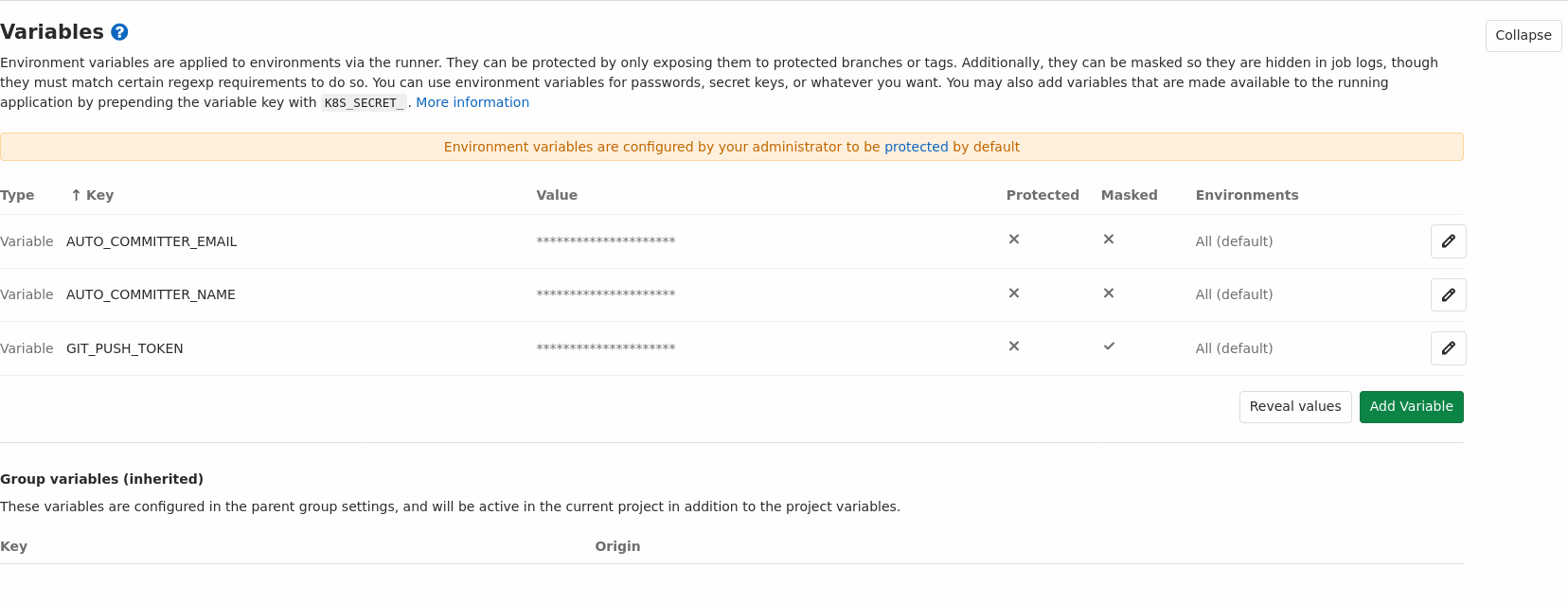
5pip-compile --upgrade requirements/base.in requirements/production.in -o requirements/production.txtFinally, we just need to define some environment variables. Go to Settings -> CI/CD and add three variables:
AUTO_COMMITTER_EMAILwhich is the email that should be assigned to the commit.AUTO_COMMITTER_NAMEwhich is the name that should be assigned to the commit.GIT_PUSH_TOKENan api token, needed for authorization to push the commit and open a merge request. To create an token navigate to User Settings -> Access Tokens and create a personal access token with api scope. The access token needs to be generated by the person who created the schedule pipeline. You may create a custom bot user, so no one has to use her own access token.
If you want to test it, navigate back to CI / CD > Schedules and click the play button to run the pipeline.
Now you have a scheduled pipeline that runs every Monday at 5 a.m., checks whether any dependency can be updated and if so it creates a merge request. This can then be approved by you and merge into the master branch. Make sure you have a good test coverage so the new versions of your dependencies do not break your code.

If you have any further questions, I made a mistake or something else you can contact me. Either write a comment or contact me via email.